The purpose of Veganism is to try to reduce as much as possible the harm to animals and to the planet by avoiding using and consuming animal-sourced products like meat, wool, honey, leather, etc. It’s often simple to know if food is vegan, based on its ingredient list.
However, other ingredients such as yeast can be more confusing. Is it a vegetable? An animal?
What is Yeast?
Yeasts are eukaryotic single-cell microorganisms that are parts of the fungus kingdom like mushrooms and molds.
As such, yeasts are neither animals nor plants.
Since yeasts are made of a single cell, their measure between 3 and 40 micrometers in diameter or about 8 times thinner than a human hair.
Yeasts reproduce by mitosis, a process where they replicate their own genetic code and split into two identical cells.
They grow by consuming available sugars such as glucose, fructose, sucrose, or maltose.
When metabolizing carbohydrates, yeast can either produce carbon dioxide and water when oxygen is available or carbon dioxide and alcohol when oxygen is depleted which is known as fermentation.
Where Is Yeast used?
Yeasts have been used in food production for several thousand years. The earliest traces of yeast used in the production of alcoholic beverages dates to about 5,000 years ago.
Since yeast produces both carbon dioxide and alcohol (though in various ratios depending on the type of fungi), it is used for:
- Alcoholic Beverages
- Baking
- Fermented Drinks
- Probiotics
Yeast in Alcoholic Beverages
The vast majority of alcoholic beverages are produced through fermentation. Therefore, wine, beer, and spirits all start by feeding the yeast with some type of sugar.
Barley makes beer, cereals or potatoes make vodka, and grapes make wine, but they all need yeast to actually produce the ethanol.
To make a beverage sparkling, the carbon dioxide byproduct of fermentation is trapped in the bottle while for flat beverages, the gas is let out.
The most common type of yeast used in winemaking and brewing is Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Yeast in Baking
The main purpose of using yeast in baking is as a leavening agent.
It works by consuming some of the carbohydrates available in the dough for the production of carbon dioxide which creates small bubbles or leaven.
Interestingly, the species of yeast used for baking is the same as the one used for alcohol fermentation, Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
However, yeast produces most of its carbon dioxide aerobically in baking, leaving very little alcohol which evaporates at common baking temperatures anyway.
Yeast is most efficient when working between 90˚F and 95˚F (32˚C to 35˚C) and dies above 120˚F (49˚C).
As a result, for optimal bread and cake rising, keep it in the oven in that temperature range. And as long as you then cook above 120˚F, there will be no yeast left in the bread.
Yeast In Non-Alcoholic Fermented Drinks
Non-alcoholic fermented drinks such as Root Beer, Kefir, or Kombucha are produced in a very similar way to alcoholic beverages.
However, the fermentation is stopped much earlier, before the yeast ran out of oxygen. As a result, yeasts have only produced trace amounts of ethanol.
Since the fermentation is cut short, fermented drinks are left with much more residual sugar than equivalent alcoholic drinks.
Yeast in Probiotics
Probiotics are nutritional supplements that are made of various types of bacteria. They occasionally contain fungi, and more specifically Saccharomyces Boulardii, a type of yeast that is known to reduce the symptoms of diarrhea.
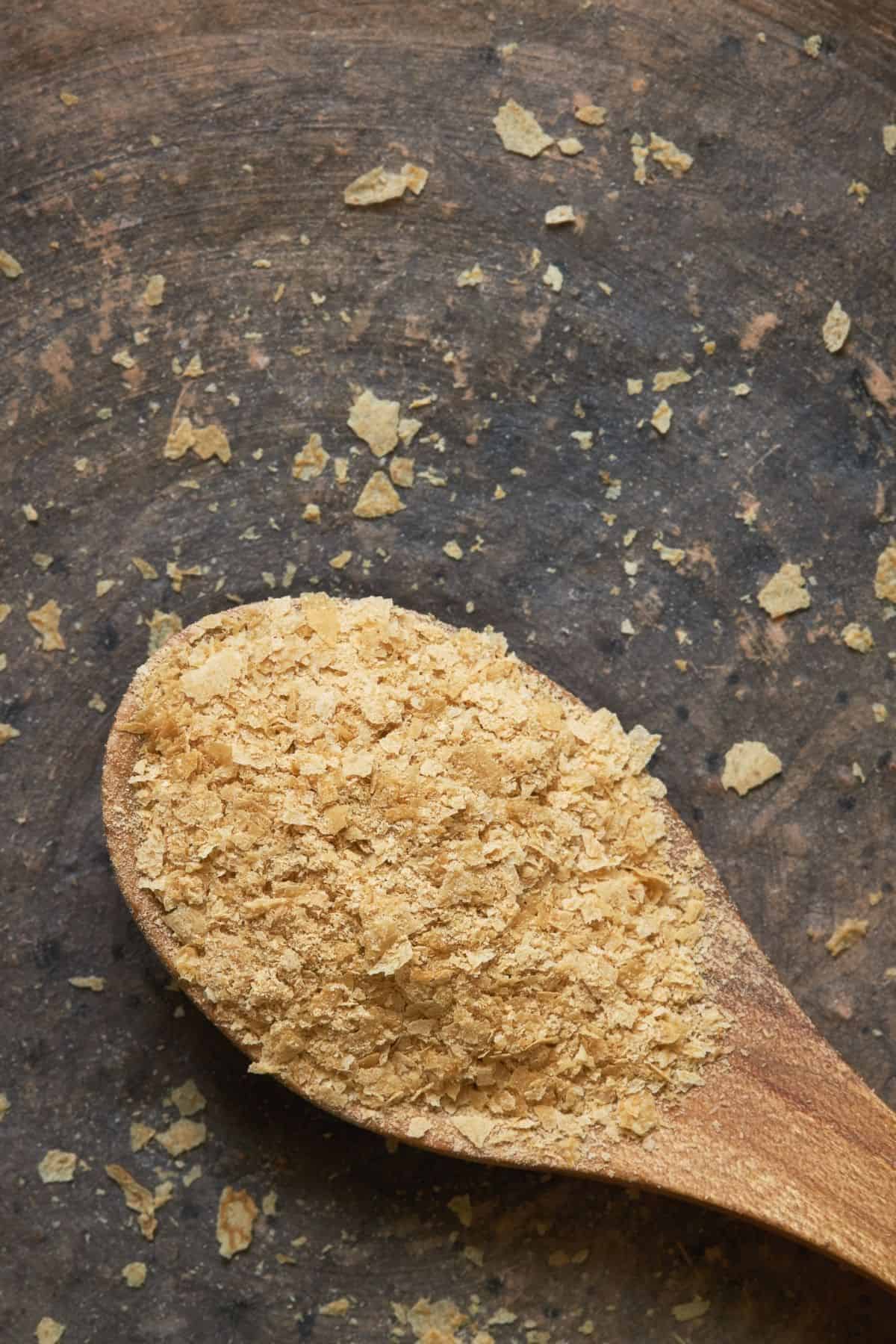
Nutritional Yeast
Nutritional Yeast or Nooch, is actually deactivated Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The same yeast species as the one used for fermentation and baking.
It is naturally rich in many essential Vitamins, and it’s often enriched in Vitamin B12.
Its cheese-like flavors make it a popular cheese substitute or taste enhancer to bring a savory taste to vegan recipes.
It’s great on popcorn, soup, miso soup, toast, or even chips.
Nutritional Yeast is one of the rare vegan-friendly complete protein sources, which means it brings all the essential amino acids that the body needs and can’t synthesize.

What Are The Different Types Of Yeast Used In Baking?
Baker’s Yeast is available in different forms: Fresh Yeast, Active Dry Yeast, and Instant Yeast.
They are all the same type of fungus, but they behave slightly differently.
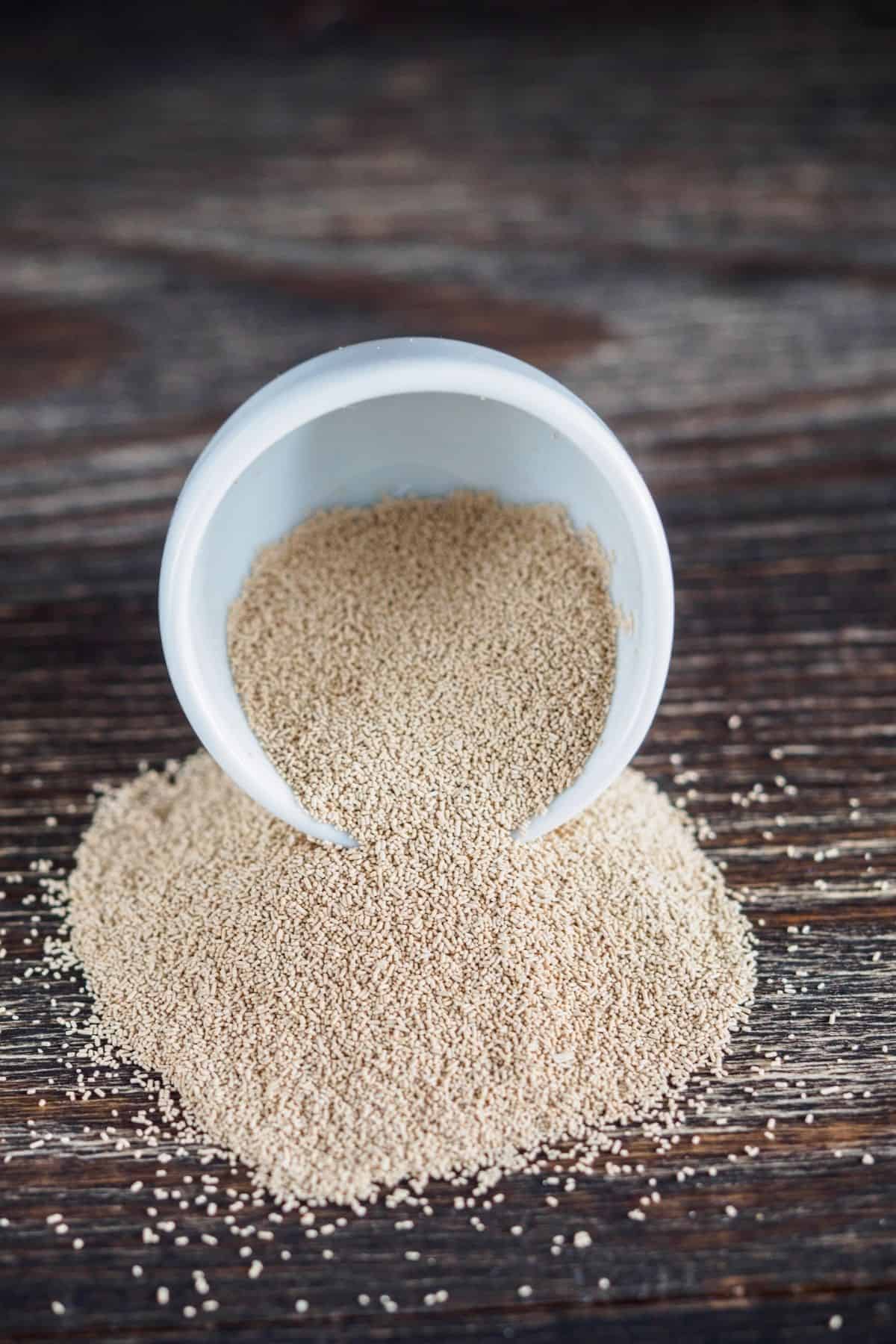
Active Dry Yeast
Active Dry Yeast is made by partially dehydrating yeast. Dehydrating the cells puts them in a dormant state for up to a few months.
Dormant yeast can then be reactivated by adding water.
Because Active Dry Yeast needs to be reactivated, it has a slower fermentation process than other types of baking yeast.
Instant Yeast
Instant Yeast is also called Bread Machine Yeast. It’s actually very similar to Active Dry Yeast.
The main difference is that the granules are much smaller which increases the contact surface of the yeast.
This allows it to absorb water much faster and reactivate quicker than Active Dry Yeast.
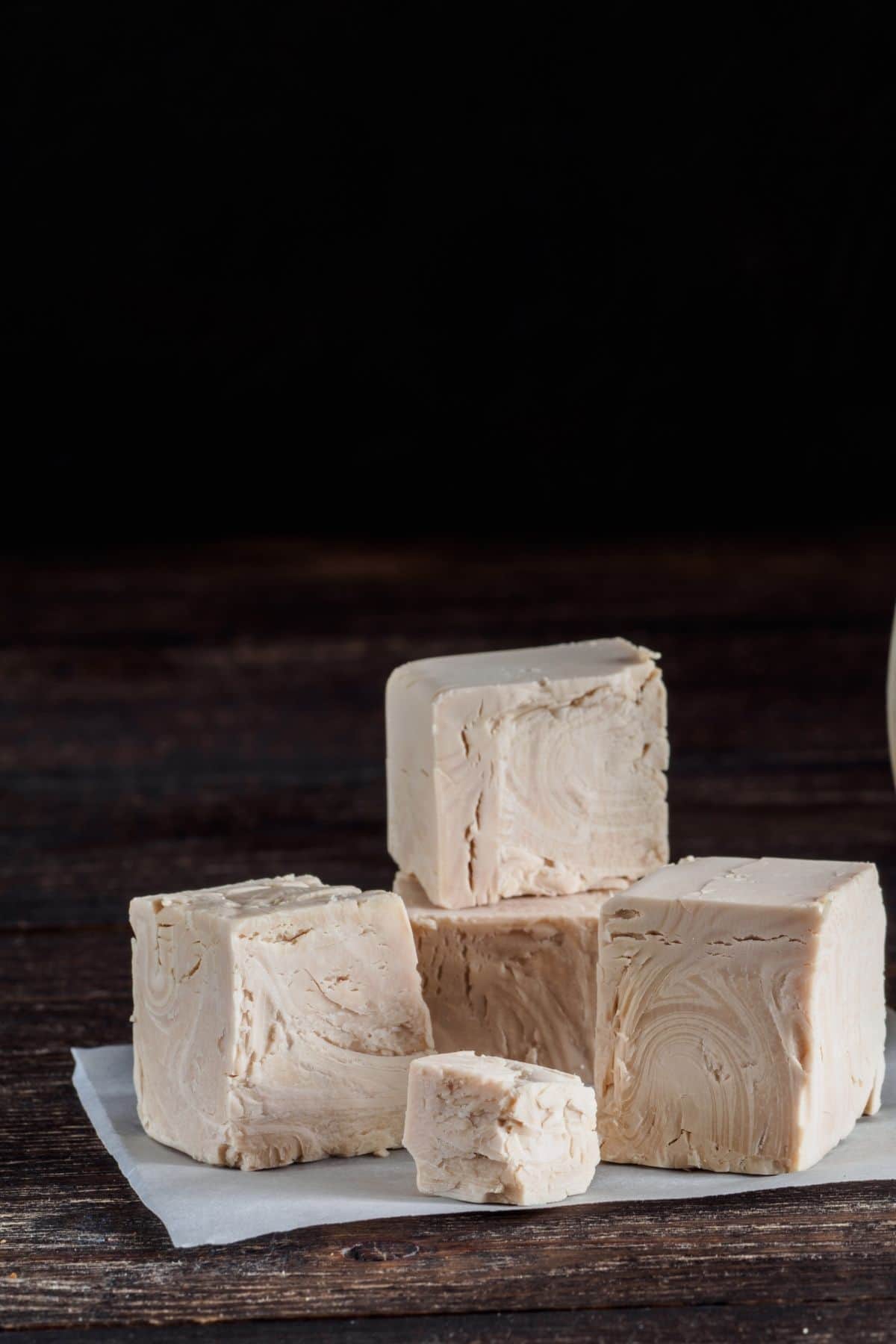
Fresh Yeast
Fresh Yeast refers to yeast in a live state. Fresh Yeast blocks are made of active organisms that are immediately ready to start the fermentation process.
It is the best yeast for bread because it produces more bubbles and has a better flavor.
However, since it’s active, it has a very short shelf-life – less than a week in the fridge.

Can Vegans Eat Yeast?
On a plant-based or vegan diet, you avoid any animal-based products. Yeast is a bacteria from the fungus kingdom, it’s therefore not an animal, though it is a living thing.
Besides, it’s quite clear that monocellular organisms are not sentient, they don’t have a central nervous system.
As a result, they are considered cruelty-free and vegan-friendly ingredients.
The process of manufacturing yeast is also largely respectful of animals and the environment. It uses two main ingredients:
- Yeast – that is essentially reproduced, so Yeast Manufacturing is like a giant fungus nursery.
- Molasse – that yeast uses as fuel to reproduce.
There are very few byproducts in yeast manufacturing. Most of them are actually recycled (ethanol, butanol).
So, yes, vegans can eat yeast.
Recipes With Yeast
We have plenty of delicious recipes with yeast!
And if you enjoy the taste of Nutritional Yeast, you can make the following recipes:
Frequently Asked Questions
Yeasts belong to the Fungus Kingdom that includes mushrooms and molds. As a result, it’s neither an animal nor a plant.
Inactive Yeast (or inactivated yeast) is a yeast that is no longer alive. As a result, inactive yeast cannot create any fermentation, it won’t make your dough rise, create any bubble, or produce ethanol.
Nutritional Yeast is a type of inactivated yeast. It is mostly used to bring flavors and vitamins to foods.
Active Yeast on the other hand is a yeast that is still capable of producing fermentation. It can be found dried (dormant) or fresh.
Activated Yeast is yeast still capable of producing fermentation. In baking, we use activated yeast to make the dough rise and create bubbles in the bread.
Yeast is considered a healthy ingredient.
It is a good source of protein, B vitamins, and minerals.
Nutritional Yeast, in particular, is a source of many essential vitamins and minerals:
– Protein: 2g per tablespoon
– Fiber: 1g per tablespoon
– Iron:2% Daily Value per tablespoon
– Thiamine (Vitamin B1): 180% Daily Value per tablespoon
– Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): 160% Daily Value per tablespoon
– Niacin (Vitamin B3): 70% Daily Value per tablespoon
– Pyridoxin (Vitamin B6): 140% Daily Value per tablespoon
– Folic Acid (Vitamin B9): 40% Daily Value per tablespoon
– Cobalamin (Vitamin B12): 40% Daily Value per tablespoon
– Panthothenic Acid (Vitamin B5): 30% Daily Value per tablespoon
– Zinc: 6% Daily Value per tablespoon
– Selenium: 10% Daily Value per tablespoon
– Potassium
– Calcium
Instant Dried Yeast, like any type of baker’s or brewer’s yeast, is 100% vegan.
Yeast Extract is made by letting the yeast cells autolyze by making their environment hypertonic. This process essentially makes the cells self-destruct, destroying their cellular walls.
Yeast Extract is the main ingredient in popular spreads such as Vegemite, Marmite, Promite, or Cenovis.
It is often used to create the umami flavor, the fifth basic flavor along sweet, sour, salty, and bitter.
Yeast is produced by letting the single-celled fungus replicate in a perfectly balanced environment.
For optimal replications, yeasts are fed with molasses and just enough oxygen. Having the right ratio of oxygen and fuel allows the yeast to sustain aerobic respiration, converting sugar into carbon dioxide and water and as little undesirable ethanol byproduct as possible.
Proofing is the act of testing that the yeast is alive before using it in a recipe. It’s a common step in baking to avoid wasting crucial bread loaf ingredients with dead yeast.
It is particularly important for fresh yeast (as it dies quickly), but you can also proof active dry yeast.
To proof yeast, follow the steps below:
1. Combine 1/2 cup of warm water (90˚F and 95˚F / 32˚C to 35˚C) with 1 tablespoon of sugar in a bowl.
2. Whisk the sugar to dissolve it completely in the water.
3. Add the yeast and stir to distribute.
4. After 10 minutes, if the bowl is covered with a creamy foam, the yeast is alive. If there’s no foam and the yeast has precipitated to the bottom of the bowl, it’s dead. Use another batch.
Yes, the yeast itself is gluten-free. To make any type of bread gluten-free, use gluten-free flour.
Conclusion: Is Yeast Vegan?
Yeast is a vegan ingredient that can be used to make delicious vegan recipes.
Nutritional yeast is a great source of essential nutrients, in particular for vegans and vegetarians.






















Leave a comment